The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
Explain the effects of price floors and price ceilings.
The price floor definition in economics is the minimum price allowed for a particular good or service.
Discuss the reasons why governments sometimes choose to control prices and the consequences of price control policies.
Price and quantity controls.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
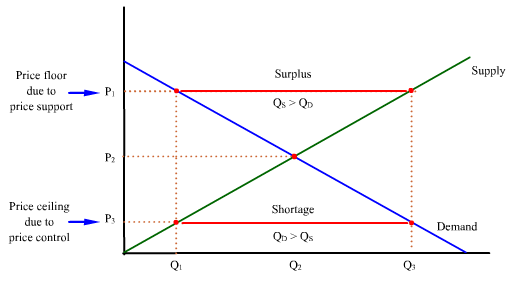
Price ceilings and price floors.
In general price ceilings contradict the free enterprise capitalist economic culture of the united states.
It may help farmers or the few workers that get to work for minimum wage but it does not always help everyone else.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
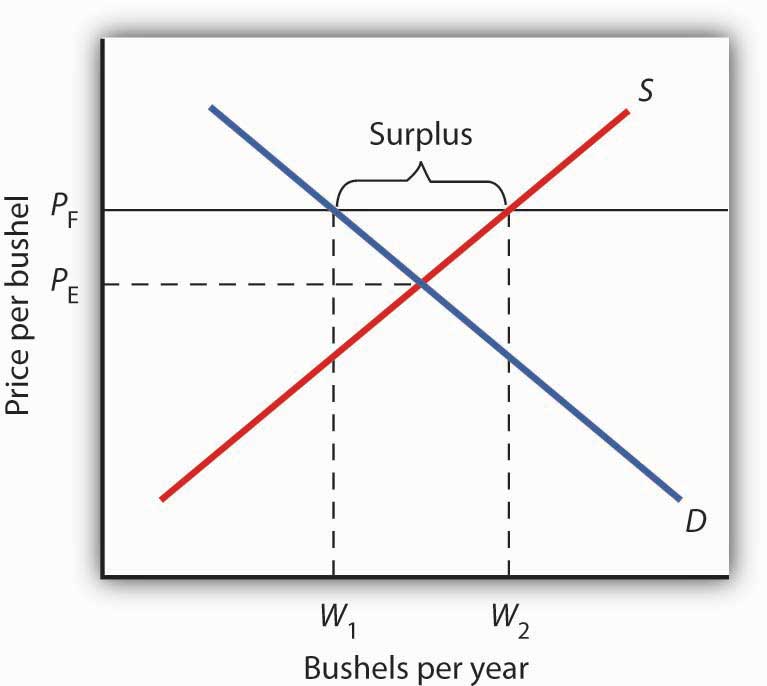
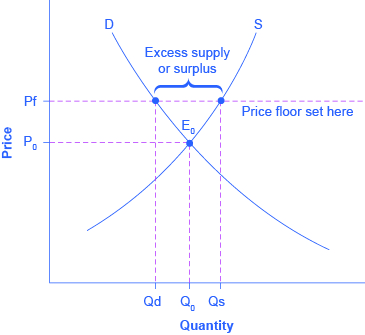
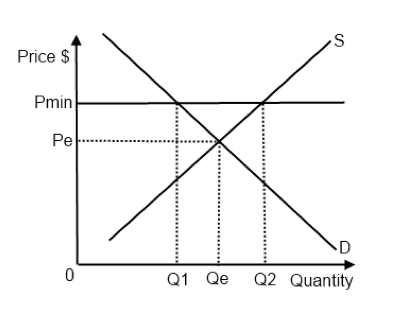
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
In the end even with good intentions a price floor can hurt society more than it helps.
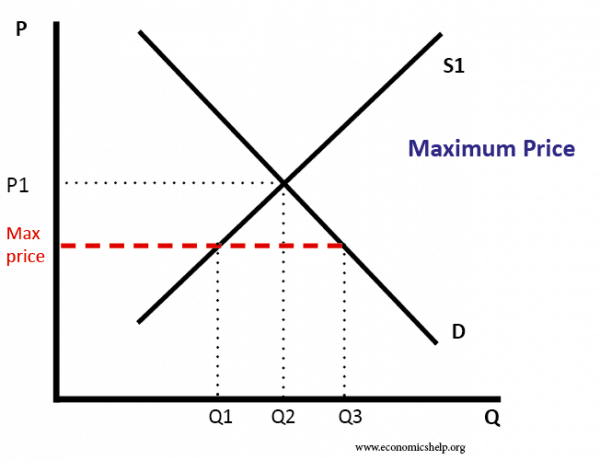
The price ceiling definition is the maximum price allowed for a particular good or service.
In other words a price floor below equilibrium will not be binding and will have no effect.
National and local governments sometimes implement price controls legal minimum or maximum prices for specific goods or services to attempt managing the economy by direct intervention price controls can be price ceilings or price floors.
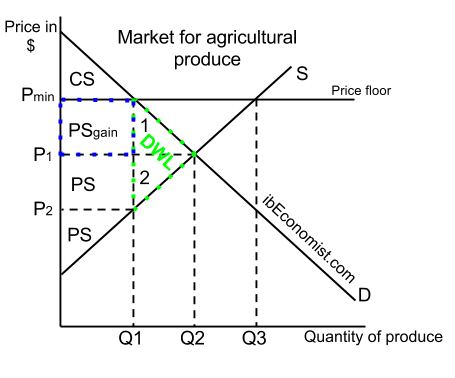
Effects of a price floor.
It s generally applied to consumer staples.
Use the model of demand and supply to explain what happens when the government imposes price floors or price ceilings.
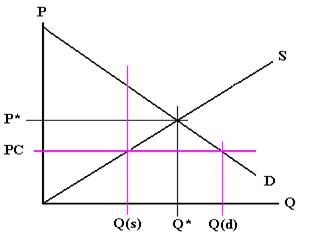
Price ceiling is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
A price ceiling is a legal maximum price but a price floor is a legal minimum price and consequently it would leave room for the price to rise to its equilibrium level.
A price ceiling is a maximum amount mandated by law that a seller can charge for a product or service.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
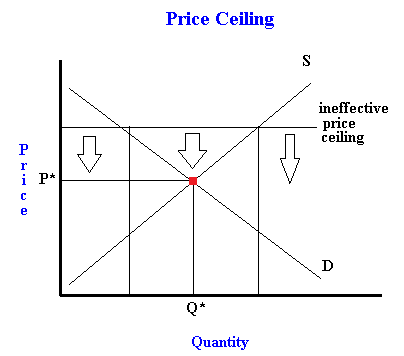
It has been found that higher price ceilings are ineffective.
A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.